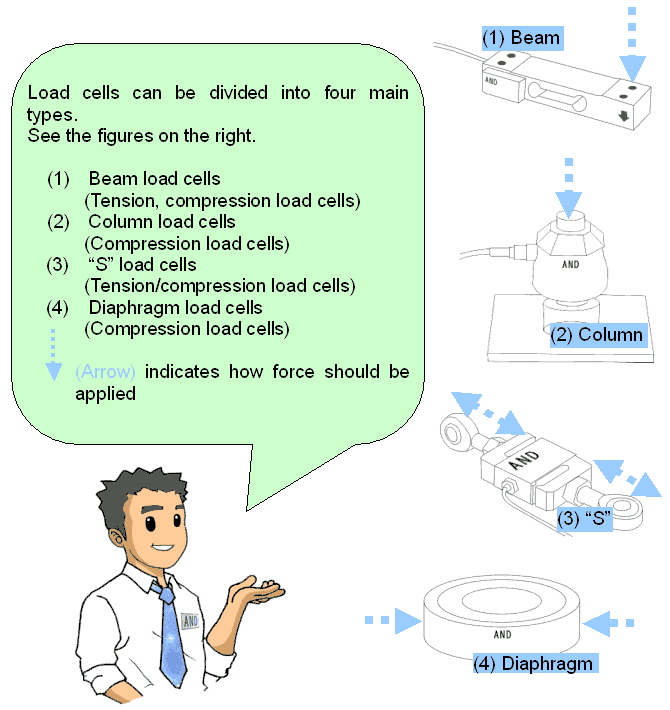
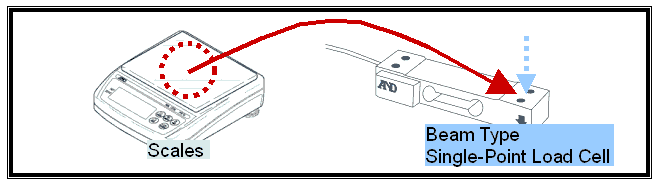
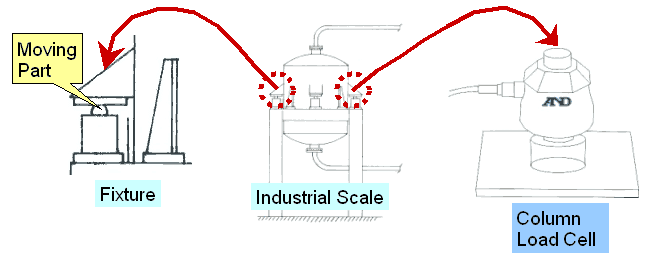
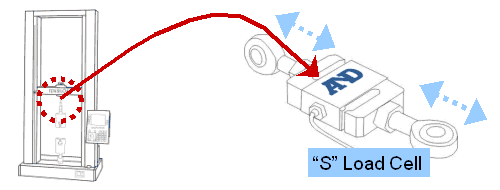
INTRODUCTION
Measuring the flow of liquids is a critical need in many industrial plants. In some operations, the ability to conduct accurate flow measurements is so important that it can make the difference between making a profit or taking a loss. In other cases, inaccurate flow measurements or failure to take measurements can cause serious (or even disastrous) results.
With most liquid flow measurement instruments, the flow rate is determined inferentially by measuring the liquid's velocity or the change in kinetic energy. Velocity depends on the pressure differential that is forcing the liquid through a pipe or conduit. Because the pipe's cross-sectional area is known and remains constant, the average velocity is an indication of the flow rate. The basic relationship for determining the liquid's flow rate in such cases is:
Q = V x A
where
Q = liquid flow through the pipe
V = average velocity of the flow
A = cross-sectional area of the pipe
Other factors that affect liquid flow rate include the liquid's viscosity and density, and the friction of the liquid in contact with the pipe.
Direct measurements of liquid flows can be made with positive-displacement flowmeters. These units divide the liquid into specific increments and move it on. The total flow is an accumulation of the measured increments, which can be counted by mechanical or electronic techniques.
Reynolds Numbers
The performance of flowmeters is also influenced by a dimensionless unit called the Reynolds Number. It is defined as the ratio of the liquid's inertial forces to its drag forces.
|
|
|
|
The flow rate and the specific gravity are inertia forces, and the pipe diameter and viscosity are drag forces. The pipe diameter and the specific gravity remain constant for most liquid applications. At very low velocities or high viscosities, R is low, and the liquid flows in smooth layers with the highest velocity at the center of the pipe and low velocities at the pipe wall where the viscous forces restrain it. This type of flow is called laminar flow. R values are below approximately 2000. A characteristic of laminar flow is the parabolic shape of its velocity profile, Fig. 1.
However, most applications involve turbulent flow, with R values above 3000. Turbulent flow occurs at high velocities or low viscosities. The flow breaks up into turbulent eddies that flow through the pipe with the same average velocity. Fluid velocity is less significant, and the velocity profile is much more uniform in shape. A transition zone exists between turbulent and laminar flows. Depending on the piping configuration and other installation conditions, the flow may be either turbulent or laminar in this zone. |
| Differential Pressure | Positive Displacement | Velocity | Mass | Open-Channel |
Orifice Plate Venturi Tube Flow Tube Flow Nozzle Pitot Tube Elbow Tap Target Variable-Area(Rotameter) | Reciprocating Piston Oval Gear Nutating Disk Rotary Vane | Turbine Vortex Shedding Swirl Conada Effect & Momentum Exchange Electromagnetic Ultrasonic, Doppler Ultrasonic, Transit-Time | Coriolis Thermal | Weir Flume |

 Numerous types of flowmeters are available for closed-piping systems. In general, the equipment can be classified as differential pressure, positive displacement, velocity, and mass meters. Differential pressure devices (also known as head meters) include orifices, venturi tubes, flow tubes, flow nozzles, pitot tubes, elbow-tap meters, target meters, and variable-area meters, Fig. 2.
Numerous types of flowmeters are available for closed-piping systems. In general, the equipment can be classified as differential pressure, positive displacement, velocity, and mass meters. Differential pressure devices (also known as head meters) include orifices, venturi tubes, flow tubes, flow nozzles, pitot tubes, elbow-tap meters, target meters, and variable-area meters, Fig. 2. Positive displacement meters include piston, oval-gear, nutating-disk, and rotary-vane types. Velocity meters consist of turbine, vortex shedding, electromagnetic, and sonic designs. Mass meters include Coriolis and thermal types. The measurement of liquid flows in open channels generally involves weirs and flumes.
Space limitations prevent a detailed discussion of all the liquid flowmeters available today. However, summary characteristics of common devices are shown in Table 1. Brief descriptions follow.
Differential Pressure Meters
The use of differential pressure as an inferred measurement of a liquid's rate of flow is well known. Differential pressure flowmeters are, by far, the most common units in use today. Estimates are that over 50 percent of all liquid flow measurement applications use this type of unit.
The basic operating principle of differential pressure flowmeters is based on the premise that the pressure drop across the meter is proportional to the square of the flow rate. The flow rate is obtained by measuring the pressure differential and extracting the square root.
Differential pressure flowmeters, like most flowmeters, have a primary and secondary element. The primary element causes a change in kinetic energy, which creates the differential pressure in the pipe. The unit must be properly matched to the pipe size, flow conditions, and the liquid's properties. And, the measurement accuracy of the element must be good over a reasonable range. The secondary element measures the differential pressure and provides the signal or read-out that is converted to the actual flow value.
Orifices are the most popular liquid flowmeters in use today. An orifice is simply a flat piece of metal with a specific-sized hole bored in it. Most orifices are of the concentric type, but eccentric, conical (quadrant), and segmental designs are also available.
In practice, the orifice plate is installed in the pipe between two flanges. Acting as the primary device, the orifice constricts the flow of liquid to produce a differential pressure across the plate. Pressure taps on either side of the plate are used to detect the difference. Major advantages of orifices are that they have no moving parts and their cost does not increase significantly with pipe size.
Conical and quadrant orifices are relatively new. The units were developed primarily to measure liquids with low Reynolds numbers. Essentially constant flow coefficients can be maintained at R values below 5000. Conical orifice plates have an upstream bevel, the depth and angle of which must be calculated and machined for each application.
The segmental wedge is a variation of the segmental orifice. It is a restriction orifice primarily designed to measure the flow of liquids containing solids. The unit has the ability to measure flows at low Reynolds numbers and still maintain the desired square-root relationship. Its design is simple, and there is only one critical dimension the wedge gap. Pressure drop through the unit is only about half that of conventional orifices.
Integral wedge assemblies combine the wedge element and pressure taps into a one-piece pipe coupling bolted to a conventional pressure transmitter. No special piping or fittings are needed to install the device in a pipeline.
Metering accuracy of all orifice flowmeters depends on the installation conditions, the orifice area ratio, and the physical properties of the liquid being measured.
Venturi tubes have the advantage of being able to handle large flow volumes at low pressure drops. A venturi tube is essentially a section of pipe with a tapered entrance and a straight throat. As liquid passes through the throat, its velocity increases, causing a pressure differential between the inlet and outlet regions.
The flowmeters have no moving parts. They can be installed in large diameter pipes using flanged, welded or threaded-end fittings. Four or more pressure taps are usually installed with the unit to average the measured pressure. Venturi tubes can be used with most liquids, including those having a high solids content.
Flow tubes are somewhat similar to venturi tubes except that they do not have the entrance cone. They have a tapered throat, but the exit is elongated and smooth. The distance between the front face and the tip is approximately one-half the pipe diameter. Pressure taps are located about one-half pipe diameter downstream and one pipe diameter upstream.
Flow Nozzles, at high velocities, can handle approximately 60 percent greater liquid flow than orifice plates having the same pressure drop. Liquids with suspended solids can also be metered. However, use of the units is not recommended for highly viscous liquids or those containing large amounts of sticky solids.
Pitot tubes sense two pressures simultaneously, impact and static. The impact unit consists of a tube with one end bent at right angles toward the flow direction. The static tube's end is closed, but a small slot is located in the side of the unit. The tubes can be mounted separately in a pipe or combined in a single casing.
Pitot tubes are generally installed by welding a coupling on a pipe and inserting the probe through the coupling. Use of most pitot tubes is limited to single point measurements. The units are susceptible to plugging by foreign material in the liquid. Advantages of pitot tubes are low cost, absence of moving parts, easy installation, and minimum pressure drop.
Elbow tap meters operate on the principle that when liquid travels in a circular path, centrifugal force is exerted along the outer edges. Thus, when liquid flows through a pipe elbow, the force on the elbow's interior surface is proportional to the density of the liquid times the square of its velocity. In addition, the force is inversely proportional to the elbow's radius.
Any 90 deg. pipe elbow can serve as a liquid flowmeter. All that is required is the placement of two small holes in the elbow's midpoint (45 deg. point) for piezometer taps. Pressure-sensing lines can be attached to the taps by using any convenient method. The difference in pressure on the outside and inside walls, caused by centrifugal force, can be measured with a differential pressure transducer. Figure 2 shows a typical installation.
Pressure measurements are obtained by placing taps at 45- degree angles on opposite sides of the elbow. The size of each of the two taps should not exceed one-eighth of the pipe diameter. Flow is calculated according to the following formula:
W = 244 [SQ.ROOT SIGN] rhD3p
where W = flow in pounds per hour
r = elbow radius (inches)
D = elbow diameter (inches)
h = differential pressure (inches H20)
p = density in lbs/ft3
Target meters sense and measure forces caused by liquid impacting on a target or drag-disk suspended in the liquid stream. A direct indication of the liquid flow rate is achieved by measuring the force exerted on the target. In its simplest form, the meter consists only of a hinged, swinging plate that moves outward, along with the liquid stream. In such cases, the device serves as a flow indicator.
A more sophisticated version uses a precision, low-level force transducer sensing element. The force of the target caused by the liquid flow is sensed by a strain gage. The output signal from the gage is indicative of the flow rate. Target meters are useful for measuring flows of dirty or corrosive liquids.
 Variable-area meters, often called rotameters, consist essentially of a tapered tube and a float, Fig. 3. Although classified as differential pressure units, they are, in reality, constant differential pressure devices. Flanged-end fittings provide an easy means for installing them in pipes. When there is no liquid flow, the float rests freely at the bottom of the tube. As liquid enters the bottom of the tube, the float begins to rise. The float is selected so as to have a density higher than that of the fluid and the position of the float varies directly with the flow rate. Its exact position is at the point where the differential pressure between the upper and lower surfaces balance the weight of the float.
Variable-area meters, often called rotameters, consist essentially of a tapered tube and a float, Fig. 3. Although classified as differential pressure units, they are, in reality, constant differential pressure devices. Flanged-end fittings provide an easy means for installing them in pipes. When there is no liquid flow, the float rests freely at the bottom of the tube. As liquid enters the bottom of the tube, the float begins to rise. The float is selected so as to have a density higher than that of the fluid and the position of the float varies directly with the flow rate. Its exact position is at the point where the differential pressure between the upper and lower surfaces balance the weight of the float.
Because the flow rate can be read directly on a scale mounted next to the tube, no secondary flow-reading devices are necessary. However, if desired, automatic sensing devices can be used to sense the float's level and transmit a flow signal. Rotameter tubes are manufactured from glass, metal, or plastic. Tube diameters vary from 1/4 to greater than 6 in.
Positive-Displacement Meters
Operation of these units consists of separating liquids into accurately measured increments and moving them on. Each segment is counted by a connecting register. Because every increment represents a discrete volume, positive-displacement units are popular for automatic batching and accounting applications. Positive-displacement meters are good candidates for measuring the flows of viscous liquids or for use where a simple mechanical meter system is needed.

Reciprocating piston meters are of the single and multiple-piston types. The specific choice depends on the range of flow rates required in the particular application. Piston meters can be used to handle a wide variety of liquids. A magnetically driven, oscillating piston meter is shown in Fig. 4. Liquid never comes in contact with gears or other parts that might clog or corrode.
Oval-gear meters have two rotating, oval-shaped gears with synchronized, close fitting teeth. A fixed quantity of liquid passes through the meter for each revolution. Shaft rotation can be monitored to obtain specific flow rates.
Nutating-disk meters have a moveable disk mounted on a concentric sphere located in a spherical side-walled chamber. The pressure of the liquid passing through the measuring chamber causes the disk to rock in a circulating path without rotating about its own axis. It is the only moving part in the measuring chamber.
A pin extending perpendicularly from the disk is connected to a mechanical counter that monitors the disk's rocking motions. Each cycle is proportional to a specific quantity of flow. As is true with all positive-displacement meters, viscosity variations below a given threshold will affect measuring accuracies. Many sizes and capacities are available. The units can be made from a wide selection of construction materials.
Rotary-vane meters are available in several designs, but they all operate on the same principle. The basic unit consists of an equally divided, rotating impeller (containing two or more compartments) mounted inside the meter's housing. The impeller is in continuous contact with the casing. A fixed volume of liquid is swept to the meter's outlet from each compartment as the impeller rotates. The revolutions of the impeller are counted and registered in volumetric units.
Helix flowmeters consist of two radically pitched helical rotors geared together, with a small clearance between the rotors and the casing. The two rotors displace liquid axially from one end of the chamber to the other.
Velocity Meters
These instruments operate linearly with respect to the volume flow rate. Because there is no square-root relationship (as with differential pressure devices), their rangeability is greater. Velocity meters have minimum sensitivity to viscosity changes when used at Reynolds numbers above 10,000. Most velocity-type meter housings are equipped with flanges or fittings to permit them to be connected directly into pipelines.

Turbine meters have found widespread use for accurate liquid measurement applications. The unit consists of a multiple-bladed rotor mounted with a pipe, perpendicular to the liquid flow. The rotor spins as the liquid passes through the blades. The rotational speed is a direct function of flow rate and can be sensed by magnetic pick-up, photoelectric cell, or gears. Electrical pulses can be counted and totalized, Fig. 5.
The number of electrical pulses counted for a given period of time is directly proportional to flow volume. A tachometer can be added to measure the turbine's rotational speed and to determine the liquid flow rate. Turbine meters, when properly specified and installed, have good accuracy, particularly with low-viscosity liquids.
A major concern with turbine meters is bearing wear. A "bearingless" design has been developed to avoid this problem. Liquid entering the meter travels through the spiraling vanes of a stator that imparts rotation to the liquid stream. The stream acts on a sphere, causing it to orbit in the space between the first stator and a similarly spiraled second stator. The orbiting movement of the sphere is detected electronically. The frequency of the resulting pulse output is proportional to flow rate.
Vortex meters make use of a natural phenomenon that occurs when a liquid flows around a bluff object. Eddies or vortices are shed alternately downstream of the object. The frequency of the vortex shedding is directly proportional to the velocity of the liquid flowing through the meter, Fig. 6.
The three major components of the flowmeter are a bluff body strut-mounted across the flowmeter bore, a sensor to detect the presence of the vortex and to generate an electrical impulse, and a signal amplification and conditioning transmitter whose output is proportional to the flow rate, Fig. 7. The meter is equally suitable for flow rate or flow totalization measurements. Use for slurries or high viscosity liquids is not recommended.
|
|
|
Swirl Meter The principle of operation of a swirl flowmeter is as follows. The meter body has a set of blades welded at the inlet, called the swirler. These blades impart a tangential velocity (or swirl) to liquids, gases or vapors. The fluid is then accelerated by a reduction in the meter body bore. A piezoelectric sensor is located in the center of the meter at the point of maximum fluid velocity. Flow is then decelerated as it approaches the meter outlet by an increase in meter body bore. A deswirler is welded to the meter body near the outlet. This deswirler eliminates the tangential velocity imparted to the fluid at the inlet so that other instrumentation downstream of the meter will not be affected by its operation.
A swirl flowmeter consists of the flowmeter body and an electronics housing (the electronics can be remote mounted for safety or convenience). Swirlmeters are only available with flanged meter bodies. A wafer option is not available, as there is for vortex meters. Swirlmeters use the same sensors and electronics as vortex meters, only the meter bodies differ in design. Swirlmeters are most cost effective with stainless steel construction, although Hastelloy is also offered. Swirlmeters are available in sizes from ½ to 16 inches, and have options for ANSI 150, 300 or 600 mating flanges.
The primary rotation caused by the swirler has at its core a low-pressure zone. The low-pressure zone is thrown into a secondary rotation proportional to flow rate. This rotating low-pressure zone can be likened to a helical coil. At low flow rates, the low-pressure swirls are farther apart (the helical coil is stretched out). At higher flows, the low-pressure swirls are closer together (the coil is compressed). Areas of slightly higher pressure separate the low-pressure swirls. The sensor will deflect (to the left and then to the right) as a pressure swirl passes from one side to other. The alternating deflection of the sensor produces a sine wave voltage output, similar to the output shown in the vortex section. The frequency of this output voltage is the same frequency as the rotating low-pressure zones, and is therefore proportional to the volumetric flow rate.
The swirl flowmeter factor does not exhibit the same deviation at high Reynolds numbers as does the vortex meter factor. This has been verified by testing on water and air at independent facilities. For this reason, a swirlmeter factor determined by water calibration is universally valid for all fluids. The swirlmeter, based on the water calibration, has a published accuracy of 0.5 percent of rate for liquids, gases or steam.
As with the vortex meter, swirlmeter rangeability is fixed by the size of the meter and the fluid properties. The sensor requires a minimum strength pressure pulse to be able to distinguish the flow signal from hydraulic noise. While turbulent flow is required at all times, the swirlmeter does not have the same limitation on Reynolds number, as does the vortex meter and can generally measure lower flows. On the other hand, the swirlmeter body presents more of an obstruction to flow than does the vortex meter, and creates higher permanent head losses under similar conditions. For this reason, the swirlmeter does not measure flow rates as high as the vortex meter. The swirlmeter, like the vortex meter, averages 10:1 turndowns or higher on liquids, and 20:1 or higher on gases and vapors. However, the flow range of a 2-inch swirlmeter will be different than the flow range of a 2-inch vortex meter under the same operating conditions. Just as for a vortex meter, you select the swirlmeter size to achieve a desired flow range given the process conditions, and never to match the process piping. Swirlmeters have to be downsized (using a 2-inch meter for 3-inch process piping) less frequently than vortex meters. Free computer software is available from manufacturers that make sizing swirl flowmeters quick and easy.
Swirl Flowmeter Application Information
Swirlmeters cost about 50 percent more than the same size vortex meter because of the added complexity and welding requirements. The rule of thumb is to use the vortex meter whenever possible for cost, and use the swirlmeter for:
- Tight piping situations.
- More viscous liquids (8 cp < μ <>
- Lower flow measurement capability.
- Higher accuracy on gases and steam.
- When downsizing to install a vortex meter is not feasible (head loss).
- These meters are compatible with low viscosity (<>
Swirlmeters are less affected by as many real world parameters as orifice plates and turbine meters, and are less sensitive to piping effects than vortex meters. Swirlmeters require just 3 diameters of straight pipe upstream (regardless of bends, valves, etc.), and either 1 or 3 diameters of straight pipe downstream (the latter only required when a control valve is downstream of the meter).
Like vortex meters, they measure velocity and infer actual volumetric flow rate from the known geometry of the meter body. Swirlmeters are generally used with flow computers to measure flow in standard volumetric or mass units (along with external pressure and/or temperature measurements). The flow computer is not necessary if the fluid density is constant. A pressure tap is provided on the meter body for making the pressure measurement (using an external sensor). The temperature element should be located downstream of the meter if needed.
The swirlmeter does not measure to true zero flow. There is a flow cut-off point below which the meter output is automatically clamped at zero (4 mA for analog output). For most applications, this limitation does not pose a problem, as the swirlmeter has good low flow capability. However, this can be a draw back for applications where flows during start-up or shutdown operations, or other upset conditions, can be greatly different than under normal operating conditions. Users may need an indication of flow under such upsets, even if they do not need to measure flow accurately, making use of the swirlmeter questionable.
Swirlmeters may also be questionable for some batching applications, especially if the pipe does not remain full between batches. The meter will not register flow as the fluid accelerates from zero to the cut-off value, and as the fluid decelerates back to zero at the end of the batch. Swirlmeters are unidirectional and will not measure or subtract any backflow from the batch total. This may create significant measurement errors, depending on the system dynamics, and the size of the batch.
There may be a potential problem installing swirlmeters on existing processes where the flow range to be measured is completely unknown. Many times, the instrument engineer makes an educated guess on flow range. A swirlmeter sized for the wrong flow range, or wrong process conditions, may need to be replaced by a different size meter entirely. Other devices, like magnetic flowmeters, orifice plates and turbine meters, are more forgiving, and can be easily adapted to fit the actual process conditions after installation.
Measuring gas flows when the process pressure is low (low-density gases) is less of a problem for swirlmeters than for vortex meters. Low-density gases can be measured with a swirlmeter, however rangeability may be less than the 20:1 mentioned previously, and extreme care must be taken in selecting the correct size meter.
Measurement of multi-phase flow has lower accuracy than for single-phase fluids. The meter will measure the flow of all phases present and report it as all liquid or gas (depending on how the meter is configured). The secondary phase should be removed, if feasible, before the meter for the highest accuracy. Any secondary phase should be homogeneously dispersed and should not have any potential for sticking to or coating the meter. There is no evidence to suggest that a swirlmeter has any advantage over a vortex meter in regards to measuring multi-phase flow.
Pressure drop must also be considered when selecting a swirlmeter. Flashing and cavitation have an adverse affect on meter accuracy, and can damage the meter itself. It was previously stated that a swirlmeter produces higher head loss than a vortex meter under the same conditions, up to five times higher. However, this is not a fair comparison. In real practice, the head loss for the swirlmeter is about the same as for the vortex meter, because you generally use a larger size swirlmeter than vortex meter to handle the same application.
Fluids that tend to form coatings are bad applications for swirlmeters.
Installation Recommendations
One of the main advantages of the swirlmeter is its insensitivity to piping effects. It is an excellent meter for tight piping situations.
Swirlmeters can be installed vertically, horizontally or at any angle. Allow liquids to flow against gravity to keep the pipe full. When the liquid is moving with gravity, elevate the downstream piping above the meter installation level to maintain a full pipe. Install the meter to avoid standing liquid when the pipe is empty. Also plan for the installation so as to avoid formation of gas bubbles in liquid flow. Check valves may be used when installing a vortex meter to keep it full of liquid when there is no active flow in the process.
Mating flanges on the process piping must be of the same nominal size as on the flowmeter. Flanges with a smooth bore, similar to weld neck flanges, are preferred. Do not use reducing flanges. Most performance specifications are based upon using Schedule 40 or Schedule 80 mating pipe. The mating pipe should be of good quality, and have an internal surface free from mill scale, pits, holes, reaming scores, bumps, etc., for a distance of 4 diameters upstream and 2 diameters downstream of the meter. The bores of the adjacent piping, meter and gaskets should be aligned to prevent steps.
Control valves should be placed no closer than 3 pipe diameters upstream or 3 pipe diameters downstream of the meter.
The sensor used in the swirlmeter can be replaced in the field, but does require process shutdown. The meter should be installed with blocking valves, or in a bypass line, if process shutdown for maintenance poses a problem.
Excessive pipe vibration or process noise can affect measurement accuracy. Mechanical pipe vibration can be eliminated by placing proper piping supports on either side of the meter, or by rotating the meter in the process piping so that the sensor is located in a plane different than the vibration. Process noise (from chattering valves, steam traps, pumps, etc.) is hydraulically connected to the meter by the fluid. The swirlmeter uses the same electronics with digital signal processing, as the vortex meter, to eliminate the adverse effects of vibration and noise, without sacrificing rangeability.
Conada Effect Flowmeter & Momentum Exchange Flowmeter. While vortex shedding flowmeters are the most recognized types of oscillating flow measurement devices, less well known are meters based on the Coanda Effect, and the phenomenon known as momentum exchange.
The Coanda Effect is named after aerodynamicist Henri-Marie Coanda, who discovered that a free jet emerging from a nozzle or conduit will follow a nearby surface and attach to it. Fluid flowing through the meter body bends toward and attaches to a sidewall. A portion of the flow is diverted through a feedback passage, however, and pushes the stream toward a sidewall on the opposite side of the meter body, which also has a feedback passage through which a portion of the flow is diverted. The fluid from this feedback passage pushes the stream back toward the sidewall to which it was initially attached, and the self-initiating, self-sustaining process is repeated. A sensor, located in one of the two feedback passages, detects the presence and absence of flow. The frequency of the pulse signals is linear with volumetric flow rate.
The momentum exchange flowmeter is similar to the Coanda model, but relies on a different mechanism to create oscillations. Unlike the Coanda meter, the momentum exchange meter does not have sidewalls. The shape of the meter body creates a main flow that passes through the nozzle and towards one side of the meter body or the other. This creates a flow pulse in a feedback passage, exerting a force on the main jet and deflecting it so it exerts a force on the fluid in the opposite passage. The pattern repeats continuously, creating a self-sustaining oscillation. Like the Coanda meter, it has a sensor in one of the feedback passages that detects the pulsing of fluids.
While most oscillating flowmeters -- including the Coanda fluidic flowmeter -- require turbulent flows to function, the momentum exchange meter does not, enabling its use with high-viscosity fluids.
Like other types of oscillating flowmeters, benefits include minimum maintenance, high stability and relatively inexpensive purchase cost. However, they are limited to use on pipes four inches in diameter or less. Use of larger pipes would create too few pulses per gallon for accurate measurement.
Electromagnetic meters can handle most liquids and slurries, providing that the material being metered is electrically conductive. Major components are the flow tube (primary element), Fig. 8. The flow tube mounts directly in the pipe. Pressure drop across the meter is the same as it is through an equivalent length of pipe because there are no moving parts or obstructions to the flow. The voltmeter can be attached directly to the flow tube or can be mounted remotely and connected to it by a shielded cable.
Electromagnetic flowmeters operate on Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction that states that a voltage will be induced when a conductor moves through a magnetic field. The liquid serves as the conductor; the magnetic field is created by energized coils outside the flow tube, Fig. 9. The amount of voltage produced is directly proportional to the flow rate. Two electrodes mounted in the pipe wall detect the voltage, which is measured by the secondary element.
Electromagnetic flowmeters have major advantages: They can measure difficult and corrosive liquids and slurries; and they can measure forward as well as reverse flow with equal accuracy. Disadvantages of earlier designs were high power consumption, and the need to obtain a full pipe and no flow to initially set the meter to zero. Recent improvements have eliminated these problems. Pulse-type excitation techniques have reduced power consumption, because excitation occurs only half the time in the unit. Zero settings are no longer required.
|
|
|
Ultrasonic flowmeters can be divided into Doppler meters and time-of-travel (or transit) meters.
Doppler meters measure the frequency shifts caused by liquid flow. Two transducers(one to transmit and the other to receive signal) are mounted in a case attached to one side of the pipe. A signal of known frequency is sent into the liquid to be measured. Solids, bubbles, or any discontinuity in the liquid, cause the pulse to be reflected to the receiver element, Fig. 10. Because the liquid causing the reflection is moving, the frequency of the returned pulse is shifted. The frequency shift is proportional to the liquid's velocity.

A portable Doppler meter capable of being operated on AC power or from a rechargeable power pack has recently been developed. The sensing heads are simply clamped to the outside of the pipe, and the instrument is ready to be used. Total weight, including the case, is 22 lb. A set of 4 to 20 millampere output terminals permits the unit to be connected to a strip chart recorder or other remote device.
Because solids particles or entrained gases are required for measurement, Doppler meters are not appropriate for clean liquids. In general, Doppler flowmeters are less accurate than TOF flowmeters, however, they are less expensive.
Time-of-travel(Transit-Time) meters have transducers mounted on each side of the pipe. The configuration is such that the sound waves traveling between the devices are at a 45 deg. angle to the direction of liquid flow. The speed of the signal traveling between the transducers increases or decreases with the direction of transmission and the velocity of the liquid being measured. A time-differential relationship proportional to the flow can be obtained by transmitting the signal alternately in both directions.
A limitation of time-of-travel meters is that the liquids being measured must be relatively free of entrained gas or solids to minimize signal scattering and absorption.
Mass Flowmeters
The continuing need for more accurate flow measurements in mass-related processes (chemical reactions, heat transfer, etc.) has resulted in the development of mass flowmeters. Various designs are available, but the one most commonly used for liquid flow applications is the Coriolis meter. Its operation is based on the natural phenomenon called the Coriolis force, hence the name.
Coriolis meters are true mass meters that measure the mass rate of flow directly as opposed to volumetric flow. Because mass does not change, the meter is linear without having to be adjusted for variations in liquid properties. It also eliminates the need to compensate for changing temperature and pressure conditions. The meter is especially useful for measuring liquids whose viscosity varies with velocity at given temperatures and pressures.
Coriolis meters are also available in various designs. A popular unit consists of a U-shaped flow tube enclosed in a sensor housing connected to an electronics unit. The sensing unit can be installed directly into any process. The electronics unit can be located up to 500 feet from the sensor.
Inside the sensor housing, the U-shaped flow tube is vibrated at its natural frequency by a magnetic device located at the bend of the tube. The vibration is similar to that of a tuning fork, covering less than 0.1 in. and completing a full cycle about 80 times/sec. As the liquid flows through the tube, it is forced to take on the vertical movement of the tube, Fig. 11. When the tube is moving upward during half of its cycle, the liquid flowing into the meter resists being forced up by pushing down on the tube.

Having been forced upward, the liquid flowing out of the meter resists having its vertical motion decreased by pushing up on the tube. This action causes the tube to twist. When the tube is moving downward during the second half of its vibration cycle, it twists in the opposite direction.
Having been forced upward, the liquid flowing out of the meter resists having its vertical motion decreased by pushing up on the tube. This action causes the tube to twist. When the tube is moving downward during the second half of its vibration cycle, it twists in the opposite direction. The ammount of twist is directly proportional to the mass flow rate of the liquid flowing through the tube. Magnetic sensors located on each side of the flow tube measure the tube velocities, which change as the tube twists. The sensors feed this information to the electronics unit, where it is processed and converted to a voltage proportional to mass flow rate. The meter has a wide range of applications from adhesives and coatings to liquid nitrogen.
This meter has extremely high accuracy but can also cause a high pressure drop.
 Thermal-type mass flowmeters have traditionally been used for gas measurements, but designs for liquid flow measurements are available. These mass meters also operate independent of density, pressure, and viscosity. Thermal meters use a heated sensing element isolated from the fluid flow path. The flow stream conducts heat from the sensing element. The conducted heat is directly proportional to the mass flow rate. The sensor never comes into direct contact with the liquid, Fig. 12. Through pre-existing built-in calibrations, the temperature differential is translated to mass flow. The accuracy of the thermal mass flow device is dependent on the reliability of the calibrations of the actual process gas or liquid and variations in the temperature, pressure, flow rate, heat capacity and viscosity of the fluid. The electronics package includes the flow analyzer, temperature compensator, and a signal conditioner that provides a linear output directly proportional to mass flow.
Thermal-type mass flowmeters have traditionally been used for gas measurements, but designs for liquid flow measurements are available. These mass meters also operate independent of density, pressure, and viscosity. Thermal meters use a heated sensing element isolated from the fluid flow path. The flow stream conducts heat from the sensing element. The conducted heat is directly proportional to the mass flow rate. The sensor never comes into direct contact with the liquid, Fig. 12. Through pre-existing built-in calibrations, the temperature differential is translated to mass flow. The accuracy of the thermal mass flow device is dependent on the reliability of the calibrations of the actual process gas or liquid and variations in the temperature, pressure, flow rate, heat capacity and viscosity of the fluid. The electronics package includes the flow analyzer, temperature compensator, and a signal conditioner that provides a linear output directly proportional to mass flow.
Open Channel Meters
The "open channel" refers to any conduit in which liquid flows with a free surface. Included are tunnels, nonpressurized sewers, partially filled pipes, canals, streams, and rivers. Of the many techniques available for monitoring open-channel flows, depth-related methods are the most common. These techniques presume that the instantaneous flow rate may be determined from a measurement of the water depth, or head. Weirs and flumes are the oldest and most widely used primary devices for measuring open-channel flows.
Weirs operate on the principle that an obstruction in a channel will cause water to back up, creating a high level (head) behind the barrier. The head is a function of flow velocity, and, therefore, the flow rate through the device. Weirs consist of vertical plates with sharp crests. The top of the plate can be straight or notched. Weirs are classified in accordance with the shape of the notch. The basic types are V-notch, rectangular, and trapezoidal.
Flumes are generally used when head loss must be kept to a minimum, or if the flowing liquid contains large amounts of suspended solids. Flumes are to open channels what venturi tubes are to closed pipes. Popular flumes are the Parshall and Palmer-Bowlus designs.
The Parshall flume consists of a converging upstream section, a throat, and a diverging downstream section. Flume walls are vertical and the floor of the throat is inclined downward. Head loss through Parshall flumes is lower than for other types of open-channel flow measuring devices. High flow velocities help make the flume self-cleaning. Flow can be measured accurately under a wide range of conditions.
Palmer-Bowlus flumes have a trapezoidal throat of uniform cross section and a length about equal to the diameter of the pipe in which it is installed. It is comparable to a Parshall flume in accuracy and in ability to pass debris without cleaning. A principal advantage is the comparative ease with which it can be installed in existing circular conduits, because a rectangular approach section is not required.
Discharge through weirs and flumes is a function of level, so level measurement techniques must be used with the equipment to determine flow rates. Staff gages and float-operated units are the simplest devices used for this purpose. Various electronic sensing, totalizing, and recording systems are also available.
Courtesy of Seil Enterprises Co.